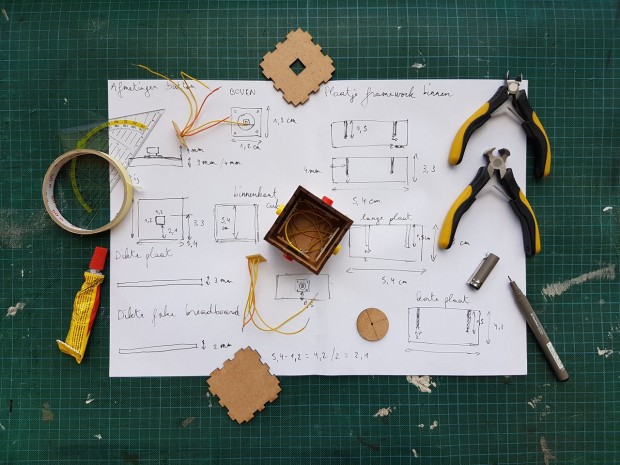
Photo : The Dynamic Benefits of Rapid Prototyping
The benefits of rapid prototyping are numerous in several categories for its convenience, speed, versatility, and reduced cost to name just a few. The process can be a bit complicated for some designs, which is what makes professional rapid prototyping services the preferred option for eliminating errors in production. One of the two basic kinds of technologies used to create prototypes is additive, which builds the piece by introducing new material it forms according to the design specs. The second is called subtractive because it starts with a preformed piece larger than the intended result and carves away what is not part of the final product.
Why Choose Additive Technology?
Additive technologies are developing very quickly thanks to the consumer craze over home versions of 3D printers creating greater interest in its improvement. The model that is the most popular and affordable uses Fused Deposition Modeling, which melts thermoplastic filament inside of a drum and then extrudes it in layers to construct a 3D model. Powder bed fusion is another additive technology, but this one creates parts by sintering or melting material with a laser on top of a build plate. SLS rapid prototyping uses Selective Laser Sintering; it is most ideal for complicated parts that are too intricate for accurate production using some other methods. Stereolithography is used for SLA rapid prototyping, which stacks photosensitive material, uses a UV light to cure each layer before starting another, and needs very little or no finish work for completion.
Subtractive Manufacturing Technology
Creating a prototype has evolved greatly over the centuries from hand carving and sculpting to modern machines that can do a remarkably better job in most cases at a fraction of the time and cost. These original techniques for creating scale replicas of other planned works are considered subtractive technology because it is removing material to achieve the desired measurements. This kind of prototype production is much faster and more economical in the modern world with the electric lathes and programmed digital automation of Computer Numerically Controlled Machining, or CNC milling. The newest innovation being utilized is lasers for cutting and engraving tasks that provide the distinct advantage of never needing to be sharpened or replaced because they have worn out.
Practical Applications
Rapid prototyping is a crucial and integrated part of every major industry including automotive, aeronautics, aerospace, consumer goods, healthcare, agriculture, and more. In fact, the digital device this article is displayed on has at least some of its parts made with this kind of technology and manufacturing. Nearly every product made from plastic started with a rapid prototyping method because of the long list of advantages this process offers at every level and run length. Selecting all of the best options for a project is a task best suited to an expert familiar with the specs and limitations of the systems. Finally, using an industry-wide standard means there are a lot of options available and more being created all the time from millions of products.
* This is a contributed article and this content does not necessarily represent the views of universityherald.com